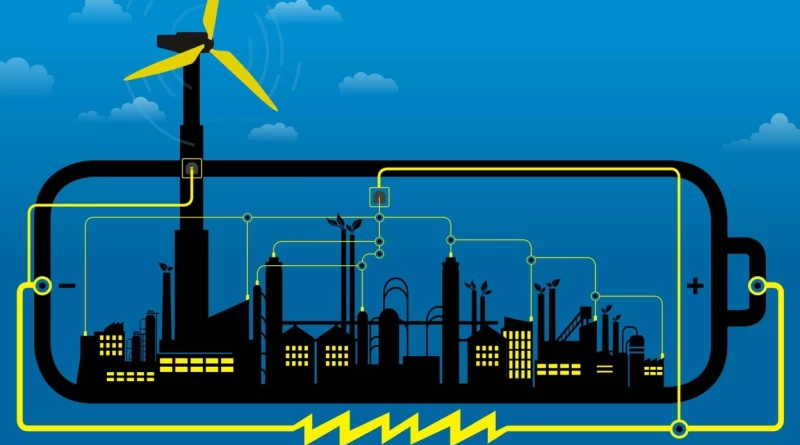
The Future of Climate Finance and Energy Transition
The future of energy transition and climate finance is expected to play a crucial role in addressing climate change and achieving global sustainability goals. Here are some key trends and developments that are likely to shape this future:
Renewable Energy Expansion: The transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal, is expected to accelerate. The falling costs of renewable technologies, coupled with increasing concerns about climate change, are driving the adoption of clean energy solutions worldwide. Governments, businesses, and individuals are investing in renewable energy projects to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote a low-carbon economy.
Energy Storage and Grid Modernization: To enable the effective integration of intermittent renewable energy sources, advancements in energy storage technologies are crucial. Battery storage systems, pumped hydro storage, and other emerging storage solutions are being developed to store surplus renewable energy and provide power during periods of high demand. Additionally, modernizing and strengthening electrical grids to accommodate decentralized and distributed energy generation is essential for a more resilient and efficient energy system.
Electrification of Transportation: The transportation sector is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. The future of energy transition involves a shift toward electric vehicles (EVs) and the deployment of charging infrastructure. Governments and industries are investing in EV manufacturing, battery technologies, and charging networks to facilitate widespread adoption of electric mobility, reducing reliance on fossil fuel-powered vehicles.
Green Infrastructure and Sustainable Cities: Building sustainable infrastructure and creating smart, energy-efficient cities are vital for a greener future. Investments in sustainable buildings, green transportation systems, efficient urban planning, and renewable energy integration within cities can significantly reduce emissions and enhance the quality of life for residents. Climate finance is expected to play a critical role in supporting these initiatives.
Climate Finance and Sustainable Investments: Climate finance refers to the mobilization of funds for projects and activities aimed at mitigating and adapting to climate change. Governments, multilateral organizations, development banks, and private sector investors are increasingly committing resources to climate finance. Financial mechanisms such as green bonds, impact investing, and sustainable investment funds are emerging as avenues to direct capital toward climate-friendly projects and technologies.
Policy and Regulatory Measures: Governments worldwide are enacting policies and regulations to support the energy transition and climate finance. These measures include carbon pricing mechanisms, renewable energy targets, energy efficiency standards, and sustainable finance regulations. Such policies provide a framework for businesses and investors, incentivizing the adoption of sustainable practices and investments.
Innovation and Collaboration: Continued innovation in clean energy technologies, climate solutions, and financial instruments will be essential. Collaboration between governments, businesses, research institutions, and civil society is crucial to foster knowledge sharing, technology transfer, and the scaling up of successful initiatives. Public-private partnerships and international cooperation will drive progress in energy transition and climate finance.
The future of energy transition and climate finance will require concerted efforts and investments to accelerate the deployment of renewable energy, enhance energy efficiency, promote sustainable infrastructure, and align financial flows with climate objectives. By leveraging technology, policy frameworks, financial mechanisms, and collaborative approaches, the world can transition to a more sustainable and climate-resilient future.